5 fully funded PhD scholarships at HT through the SEMM
Human Technopole is offering up to 5 fully funded PhD scholarships to young scientists from the national and international community who wish to undertake a doctoral degree on a project focused on Computational Biology, Structural Biology or Biophysical modelling.
Multiscale investigation of 7q11.23 copy number variation in neurodevelopmental disorders
Using diverse omics approaches and multiscale disease modelling, Human Technopole researchers uncovered the effects of 7q11.23 CNV, a section of chromosome 7 on neuronal differentiation, gene expression, protein synthesis, and intrinsic neuronal excitability in two neurodevelopmental disorders (i.e., Williams-Beuren and 7q microduplication syndromes). The research results are published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
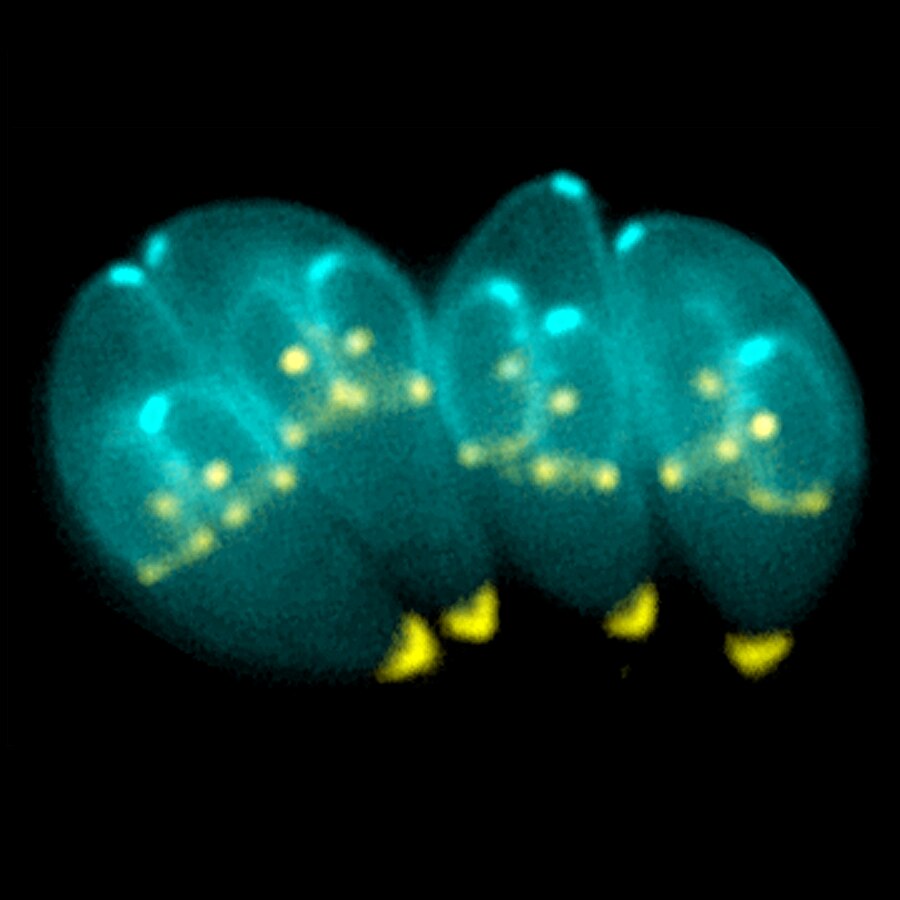
Engineered Parasite Delivers Therapeutic Proteins to Central Nervous System
Engineering a parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, which is naturally suited to cross the blood-brain barrier and enter neuronal cells, so that it can deliver therapeutic proteins to the central nervous system: this is the result of a study by an international group of scientists, including researchers from the University of Milan and Human Technopole, recently published in Nature Microbiology.
Chan Zuckerberg Initiative grant to the Glastonbury Group
The Glastonbury Group is among the recipients of the Data Insights Cycle 3 awards. The aim of the grant is to develop a machine learning model that identifies disease-relevant cell subpopulations whilst predicting a phenotype/disease of interest from large-scale single-cell RNA-seq data.
Understanding the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 encephalitis
In collaboration with an international team of scientists, HT researchers identified a missense mutation in a gene involved in brain-intrinsic immunity as the genetic cause of SARS-CoV-2 brainstem encephalitis.