Zerial Group
Il gruppo Zerial studia i meccanismi molecolari dell’organizzazione cellulare e dei tessuti. La nostra ricerca attraversa le scale biologiche e le discipline per decifrare le interazioni tra proteine all’interno del macchinario di fusione endosomiale, definire i processi che stabiliscono la polarità degli epatociti e comprendere la biofisica della formazione del tessuto epatico. Infine, sfruttiamo la nostra conoscenza della delicata interazione tra forze, molecole e cellule per trovare soluzioni innovative per il delivery di farmaci.
Per maggiori informazioni sulla ricerca di Zerial, visita il sito web del Gruppo.
Non trovi una posizione per te nella nostra pagina Careers? Contattaci comunque! Vogliamo ascoltare la tua proposta di ricerca!
Contatto: [email protected]
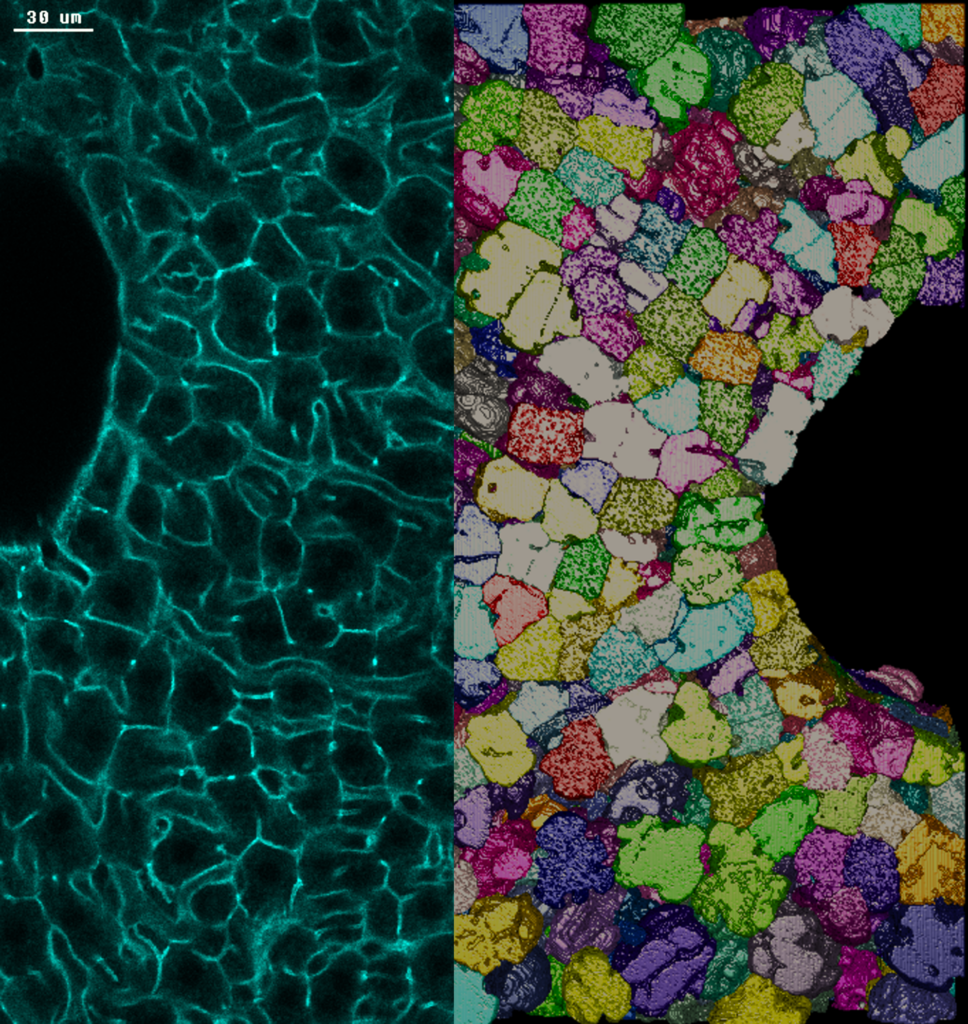
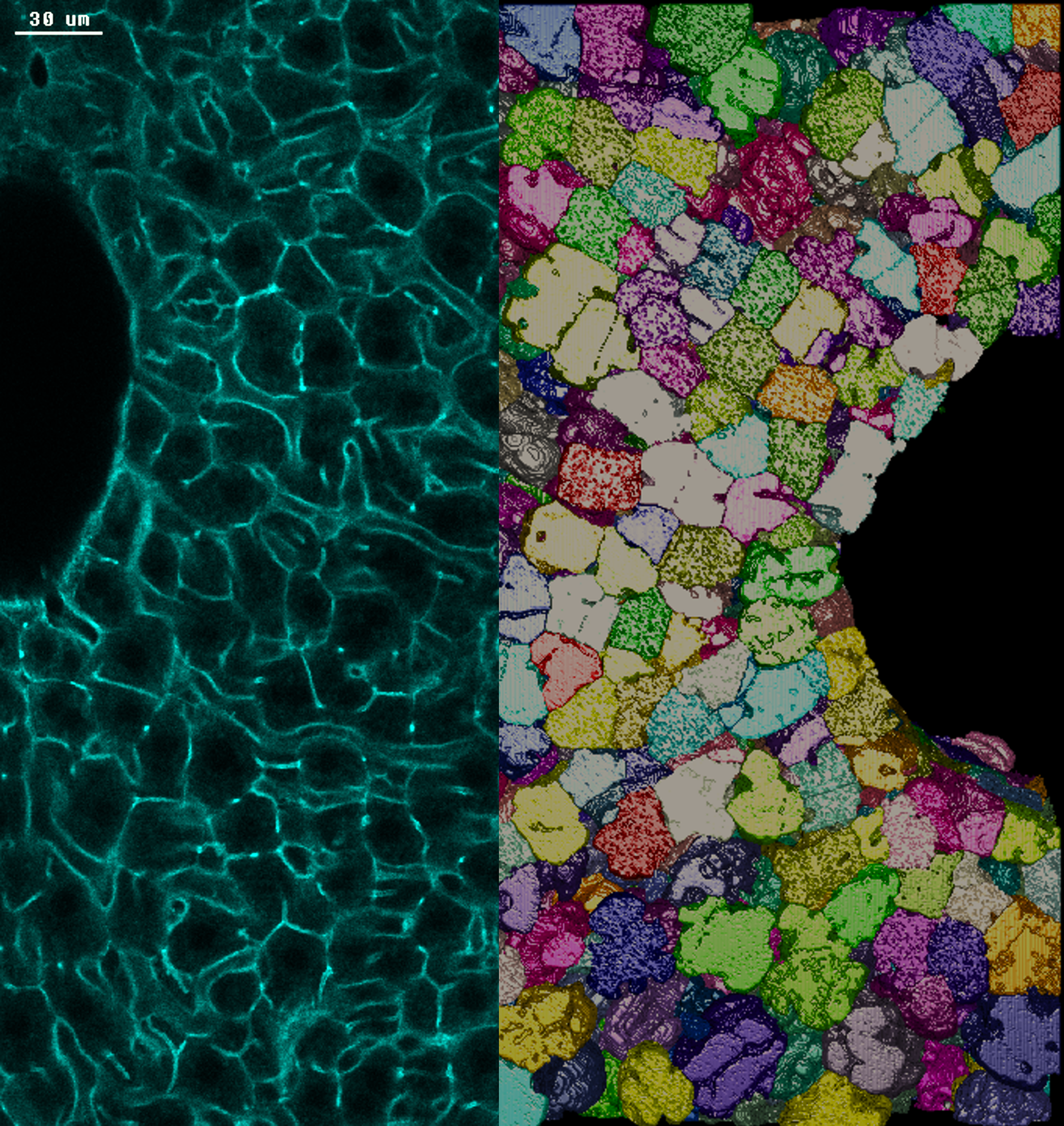
Photo credits: Nuno Pimpao Martins / MPI-CBG. A sinistra: sezione di tessuto epatico di topo adulto colorato con actina. I confini delle cellule tra due grandi vene sono evidenziati in verde. A destra: ricostruzione tridimensionale dei confini degli epatociti, le principali cellule metaboliche del fegato.
Membri del gruppo
-
 Marino Zerial
Marino Zerial
Director -
 Zhansaya Bauyrzhanova
Zhansaya Bauyrzhanova
PhD Student -
 Marta La Bruna
Marta La Bruna
PhD Student -
 Ilaria Raimondi
Ilaria Raimondi
Technician -
 Lidan Shi
Lidan Shi
Postdoc -
 Chiara Ticli
Chiara Ticli
Postgraduate Fellow -
 José Ignacio Valenzuela Iturra
José Ignacio Valenzuela Iturra
Staff Scientist
Pubblicazioni
-
05/2023 - Nature Physics
Two-component molecular motor driven by a GTPase cycle
ATPases are a group of enzymes that can cyclically convert the free energy of ATP hydrolysis into mechanical work. GTPases are another class of enzymes that are predominantly associated with signal transduction processes, but their role in mechanotransduction is less established. It was previously shown that the binding of the GTPase Rab5 to the tethering […]
-
12/2019
Three-dimensional spatially resolved geometrical and functional models of human liver tissue reveal new aspects of NAFLD progression
Early disease diagnosis is key to the effective treatment of diseases. Histopathological analysis of human biopsies is the gold standard to diagnose tissue alterations. However, this approach has low resolution and overlooks 3D (three-dimensional) structural changes resulting from functional alterations. Here, we applied multiphoton imaging, 3D digital reconstructions and computational simulations to generate spatially resolved […]
-
08/2016 - Nature
An endosomal tether undergoes an entropic collapse to bring vesicles together
An early step in intracellular transport is the selective recognition of a vesicle by its appropriate target membrane, a process regulated by Rab GTPases via the recruitment of tethering effectors1,2,3,4. Membrane tethering confers higher selectivity and efficiency to membrane fusion than the pairing of SNAREs (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) alone5,6,7. Here we address the […]
-
05/2012 - Nature
Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo
An outstanding question is how cells control the number and size of membrane organelles. The small GTPase Rab5 has been proposed to be a master regulator of endosome biogenesis. Here, to test this hypothesis, we developed a mathematical model of endosome dependency on Rab5 and validated it by titrating down all three Rab5 isoforms in […]
-
05/2009 - Nature
Reconstitution of Rab- and SNARE-dependent membrane fusion by synthetic endosomes
Rab GTPases and SNAREs (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) are evolutionarily conserved essential components of the eukaryotic intracellular transport system. Although pairing of cognate SNAREs is sufficient to fuse membranes in vitro, a complete reconstitution of the Rab–SNARE machinery has never been achieved. Here we report the reconstitution of the early endosomal canine Rab5 GTPase, its […]