Vannini Group
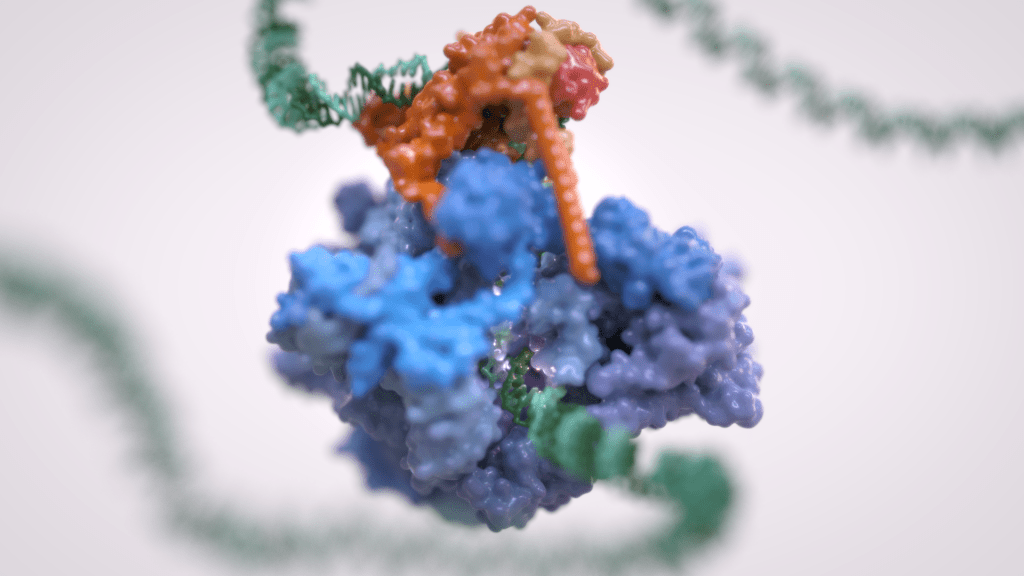
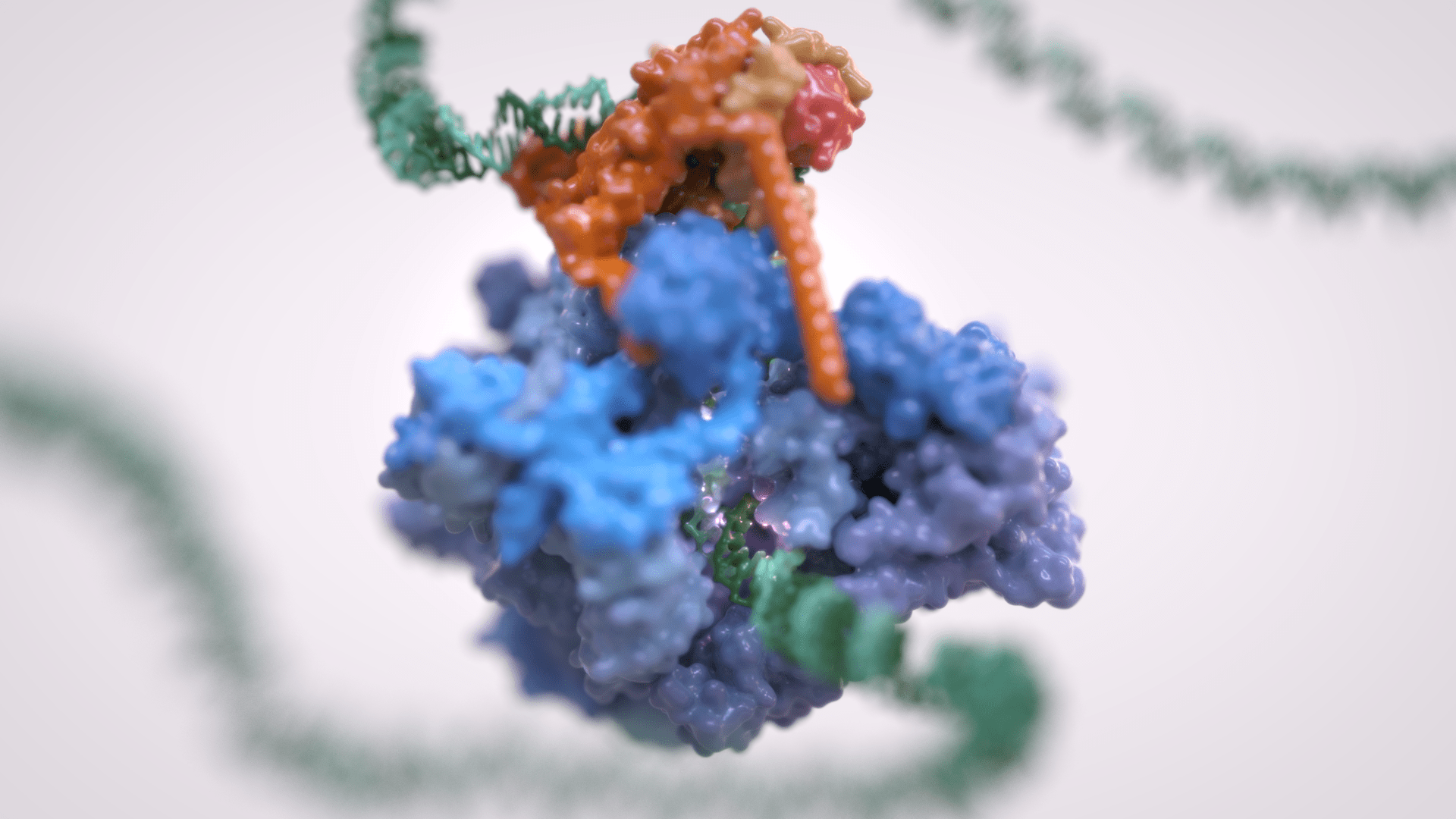
Gene transcription is the first step that controls the expression of the genetic information encoded in a genome and ultimately underlies cell differentiation and organism development. Eukaryotic gene transcription occurs in the context of highly structured and organised genomes and acts as a coordinator of numerous events co-occurring in the nucleus. Eukaryotic transcription relies on three different RNA polymerases: RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcribes ribosomal RNA, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) synthesizes messenger RNAs and RNA polymerase III (Pol III) produces short and non-translated RNAs, including the entire pool of tRNAs, which are essential for cell growth.
For a long time, it was assumed that only Pol II was regulated whereas Pol I and Pol III did not require such control. However, it is now clear that RNA polymerase III transcription is tightly regulated and a determinant of organismal growth. Pol III deregulation is observed in many forms of cancer and Pol III genetic mutations cause severe neurodegenerative diseases.
Furthermore, Pol III and its associated factors play a paramount role into genome structure and organisation. These “extra-transcriptional roles” are carried out throughout interactions with other cellular components such as retroelement transposition machineries, Structural Maintenance of Chromosome (SMC) complexes and specific chromatin remodellers.
The Vannini Group employs an Integrative Structural Biology approach, combining cutting-edge cryo-EM analysis, x-ray diffraction data, cross-linking and native mass-spectrometry. We integrate the structural data with molecular and cellular biology techniques in order to obtain a comprehensive view of these fundamental processes and how their mis-regulation can lead to cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
Group members
-
 Alessandro Vannini
Alessandro Vannini
Head of Structural Biology Research Centre -
 Alessandro Borsellini
Alessandro Borsellini
Postdoc -
 Giacomo Ettore Casale
Giacomo Ettore Casale
Postdoc -
 Valentina Cecatiello
Valentina Cecatiello
Senior Technician -
 Sebastian Chamera
Sebastian Chamera
Postdoc -
 Fabiola Iommazzo
Fabiola Iommazzo
PhD Student -
 Thomas Noé Perry
Thomas Noé Perry
Postdoc -
 Fabio Pessina
Fabio Pessina
Senior Technician -
 Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Postdoc -
 Ewan Ramsay
Ewan Ramsay
Senior Staff Scientist -
 Ankit Roy
Ankit Roy
PhD Student -
 Syed Zawar Shah
Syed Zawar Shah
PhD Student
Publications
-
08/2002 - Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the transcriptional regulator TraR bound to its cofactor and to a specific DNA sequence
TraR is an Agrobacterium tumefaciens transcriptional regulator which binds the pheromone N-3-oxooctanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (AAI) in response to the bacterial population density. The TraR-AAI complex dimerizes and interacts with a specific 18-base-pair DNA sequence (TraBox), activating promoters containing this site. TraR was overexpressed and purified from Escherichia coli. Crystals of the ternary complex, in which dimeric […]
-
12/2001 - Eur J Biochem
Effect of ibuprofen and warfarin on the allosteric properties of haem-human serum albumin. A spectroscopic study
Haem binding to human serum albumin (HSA) endows the protein with peculiar spectroscopic properties. Here, the effect of ibuprofen and warfarin on the spectroscopic properties of ferric haem-human serum albumin (ferric HSA-haem) and of ferrous nitrosylated haem-human serum albumin (ferrous HSA-haem-NO) is reported. Ferric HSA-haem is hexa-coordinated, the haem-iron atom being bonded to His105 and […]
-
06/2001 - J Biol Inorg Chem
Relaxometric characterization of human hemalbumin
Hemalbumin [i.e., Fe(III)-protoporphyrin IX-human serum albumin; Fe(III)heme-HSA] is an important intermediate in the recovery of heme iron following hemolysis. Relaxometric data are consistent with the occurrence of a hexacoordinated high-spin Fe(III) center with no water in the inner coordination sphere. The relatively high relaxation enhancement observed for an aqueous solution of Fe(III)heme-HSA (r1p=4.8 mM(-1)s(-1) at […]
-
04/2001 - J Inorg Biochem
Effect of bezafibrate and clofibrate on the heme-iron geometry of ferrous nitrosylated heme-human serum albumin: an EPR study
The effect of bezafibrate (BZF) and clofibrate (CF), two therapeutic drugs displaying anticoagulant and antihyperlipoproteinemic activities, on the EPR-spectroscopic properties of ferrous nitrosylated heme-human serum albumin (HSA-heme-NO) has been investigated. In the absence of BZF and CF, HSA-heme-NO is a five-coordinate heme-iron system, characterised by an X-band EPR spectrum with a three-line splitting in the […]