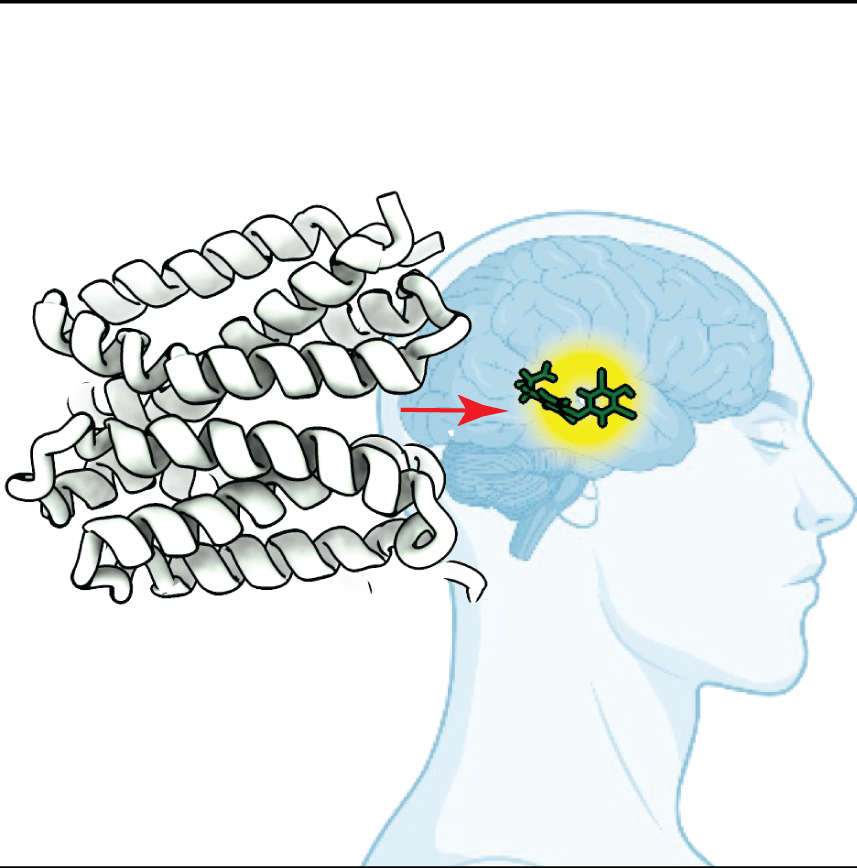
How thyroid hormones are transported into target cells
An international collaboration between Human Technopole and Erasmus Medical Centre researchers sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the transport of thyroid hormones in human cells by monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs). The results of the research are published in Nature Communications.
HT National Facilities: Upcoming Call for Access 2025 – Round 2
On 27 and 28 March, the SIEC (Standing Independent Evaluation Committee), visited HT to discuss the results of the first call for access, which was considered a pilot phase, and refine the upcoming call, planned to be published at the beginning of June 2025.
HT PhD Student & Postdoc Symposium 2025: “Research in Motion”
After the success of its inaugural edition, which gathered over 100 participants, the HT PhD Student & Postdoc Symposium returns for its second year on 30 September 2025. Join us in supporting the future of life sciences. Every contribution can make a difference!
Cancer, insomnia, ancient DNA: over 100 projects from Italian scientists at HT
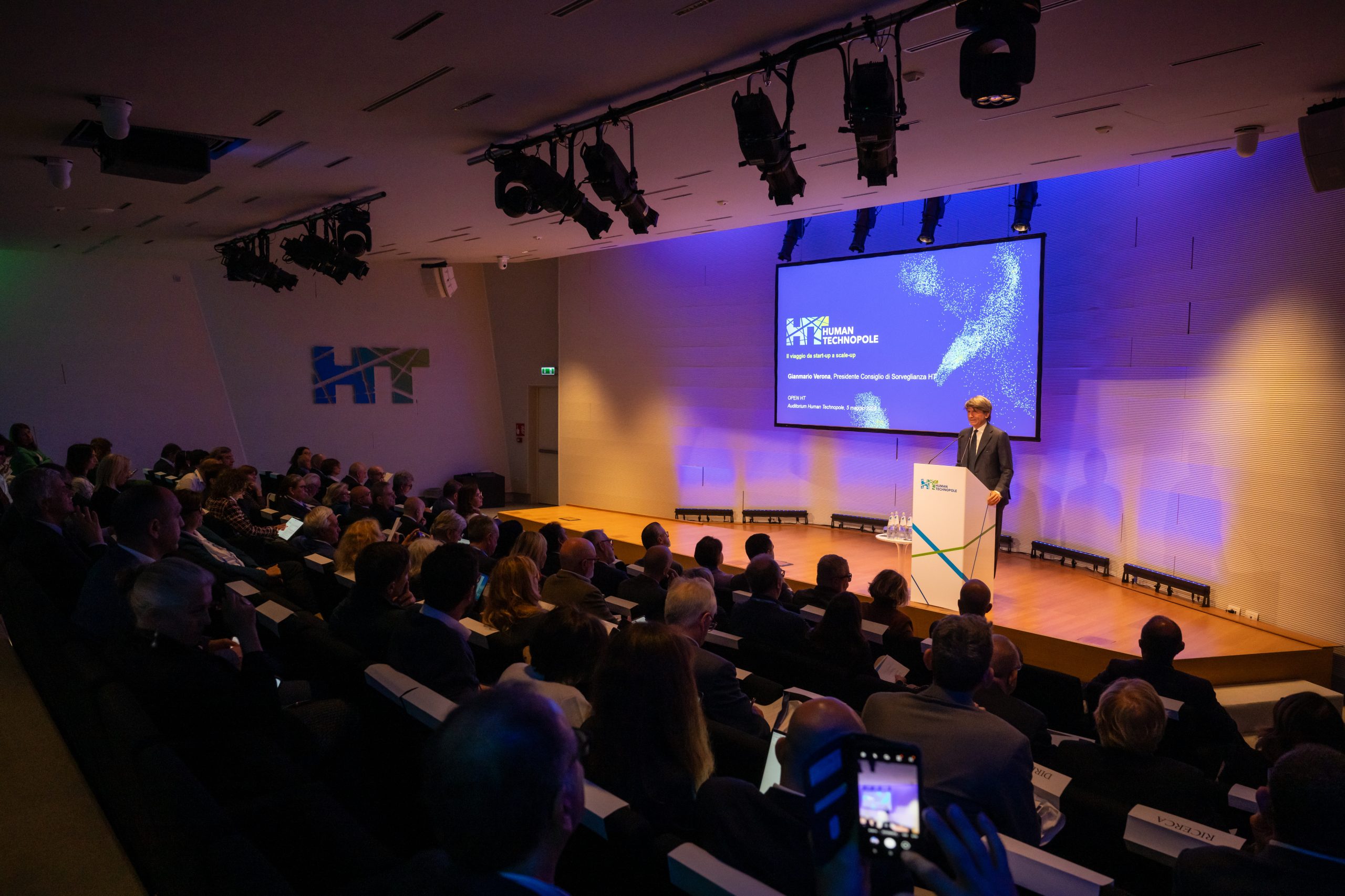
Human Technopole has presented 102 research projects that were the first to benefit from the cutting-edge equipment of the National Facilities — the advanced technologies that the Institute makes available to external researchers from across Italy. The majority of studies focus on cancer and neurodegenerative diseases, accounting for 50% of the selected projects. The announcement was made this morning in Milan during “Open HT – The Open Day on Life Sciences”, an event designed to showcase Human Technopole’s achievements and outline future goals.
PhD Opportunity in Data Science for Medicine
Human Technopole is looking for a curious, driven, and collaborative PhD candidate to join the Research group lead by Fernanda Pinheiro as part of the EU-funded ENDAMR (Exploring Novel Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance), a Marie Skłodowska Curie Actions (MSCA) Doctoral Network. This PhD project will develop mechanistic models grounded on microbial physiology to understand how interactions among mutually dependent bacteria influence antibiotic tolerance, community-level perturbations and evolutionary trajectories toward antimicrobial resistance.