Vannini Group
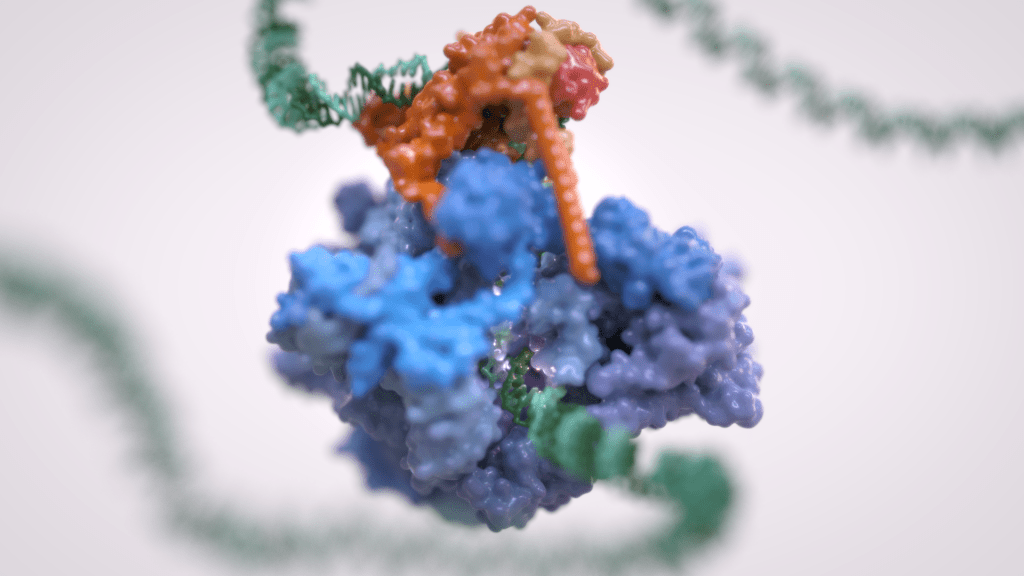
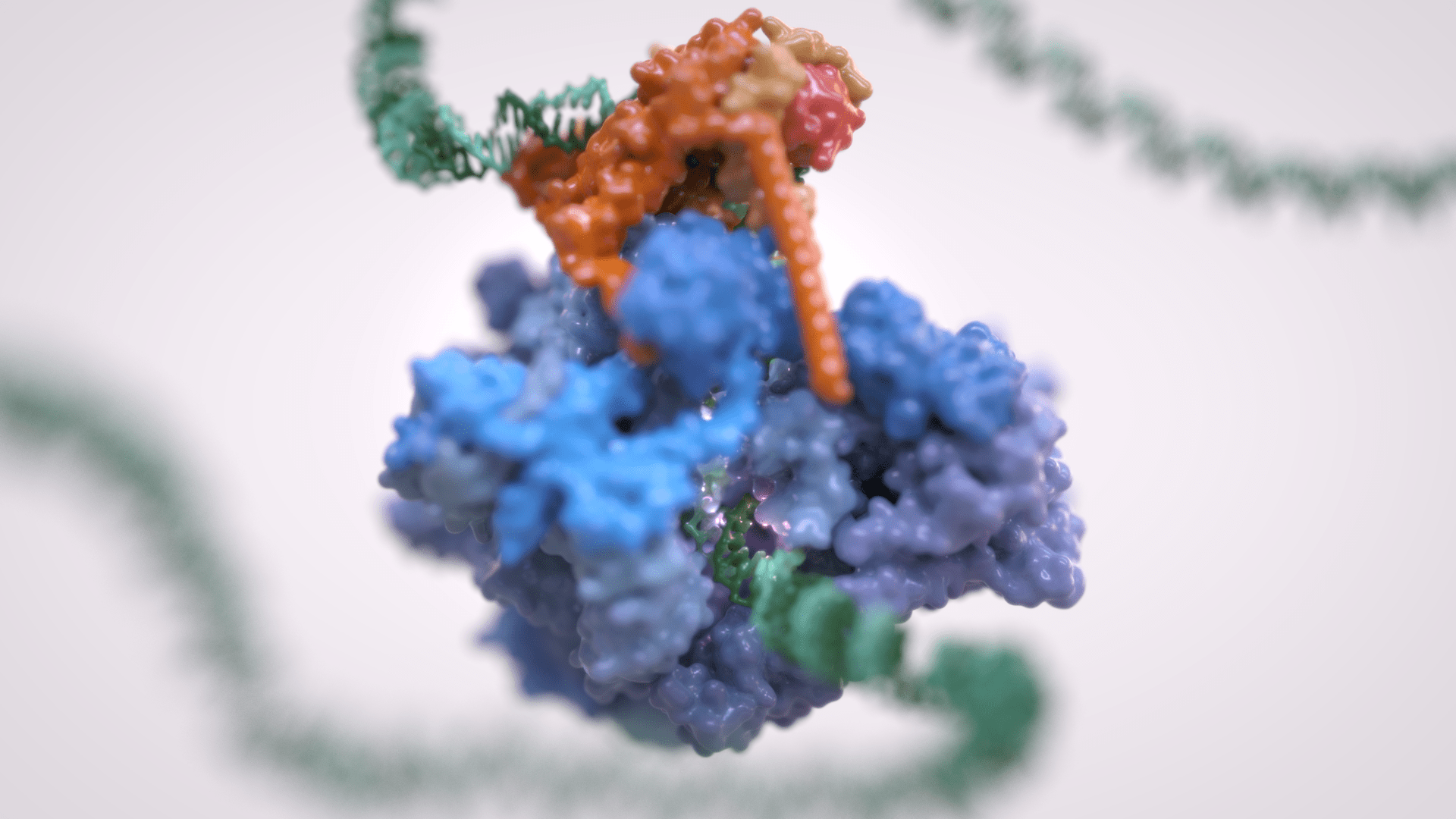
La trascrizione genica è il primo passaggio che regola l’espressione dell’informazione genetica codificata in un genoma, ed è alla base della differenziazione cellulare e dello sviluppo dell’organismo. La trascrizione genica eucariotica avviene nel contesto di genomi altamente strutturati e organizzati e coordina numerosi eventi che si verificano nel nucleo. La trascrizione eucariotica si basa su tre diverse RNA polimerasi: L’RNA polimerasi I (Pol I) trascrive l’RNA ribosomiale, l’RNA polimerasi II (Pol II) sintetizza gli RNA messaggeri e l’RNA polimerasi III (Pol III) produce RNA brevi e non tradotti, compreso l’intero pool di tRNA, che sono essenziali per la crescita cellulare.
Per molto tempo si è ritenuto che solo Pol II fosse regolata e che Pol I e Pol III non richiedessero tale controllo, essendo dedicati a geni housekeeping. Tuttavia, è ora chiaro come la trascrizione dell’RNA polimerasi III sia strettamente regolata e sia un fattore determinante per la crescita di un organismo. La deregolazione di Pol III è stata osservata in varie forme di cancro e mutazioni genetiche a carico di Pol III causano gravi malattie neurodegenerative.
Inoltre, Pol III e i suoi fattori associati svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nella struttura e nell’organizzazione del genoma. Questi “ruoli extra-trascrizionali” sono svolti attraverso interazioni con altri componenti cellulari quali i transposoni, i complessi SMC (dall’inglese Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) e i rimodellatori specifici della cromatina.
Il Vannini Group utilizza un approccio di Biologia Strutturale Integrativa, che combina analisi di crio-microscopia elettronica all’avanguardia, dati di diffrazione dei raggi X, cross-linking e spettrometria di massa nativa. Integriamo i dati strutturali con le tecniche di biologia molecolare e cellulare per ottenere una visione globale di questi processi fondamentali e di come la loro errata regolazione possa condurre a malattie oncologiche e neurodegenerative.
Membri del gruppo
-
 Alessandro Vannini
Alessandro Vannini
Head of Structural Biology Research Centre -
 Alessandro Borsellini
Alessandro Borsellini
Postdoc -
 Giacomo Ettore Casale
Giacomo Ettore Casale
Postdoc -
 Valentina Cecatiello
Valentina Cecatiello
Senior Technician -
 Sebastian Chamera
Sebastian Chamera
Postdoc -
 Fabiola Iommazzo
Fabiola Iommazzo
PhD Student -
 Thomas Noé Perry
Thomas Noé Perry
Postdoc -
 Fabio Pessina
Fabio Pessina
Senior Technician -
 Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Postdoc -
 Ewan Ramsay
Ewan Ramsay
Senior Staff Scientist -
 Ankit Roy
Ankit Roy
PhD Student -
 Syed Zawar Shah
Syed Zawar Shah
PhD Student
Pubblicazioni
-
11/2022 - Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
Structural basis of SNAPc-dependent snRNA transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) carries out transcription of both protein-coding and non-coding genes. Whereas Pol II initiation at protein-coding genes has been studied in detail, Pol II initiation at non-coding genes, such as small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, is less well understood at the structural level. Here, we study Pol II initiation at snRNA […]
-
09/2022 - Life Sci Alliance
The human RNA polymerase I structure reveals an HMG-like docking domain specific to metazoans
Transcription of the ribosomal RNA precursor by RNA polymerase (Pol) I is a major determinant of cellular growth, and dysregulation is observed in many cancer types. Here, we present the purification of human Pol I from cells carrying a genomic GFP fusion on the largest subunit allowing the structural and functional analysis of the enzyme […]
-
12/2021 - Elife
MCPH1 inhibits Condensin II during interphase by regulating its SMC2-Kleisin interface
Dramatic change in chromosomal DNA morphology between interphase and mitosis is a defining features of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Two types of enzymes, namely cohesin and condensin confer the topology of chromosomal DNA by extruding DNA loops. While condensin normally configures chromosomes exclusively during mitosis, cohesin does so during interphase. The processivity of cohesin’s loop […]
-
11/2021 - Nature Communications
Structural basis of Ty3 retrotransposon integration at RNA Polymerase III-transcribed genes
Retrotransposons are endogenous elements that have the ability to mobilise their DNA between different locations in the host genome. The Ty3 retrotransposon integrates with an exquisite specificity in a narrow window upstream of RNA Polymerase (Pol) III-transcribed genes, representing a paradigm for harmless targeted integration. Here we present the cryo-EM reconstruction at 4.0 Å of […]
-
09/2021 - Molecular Cell
A small nucleosome from a weird virus with a fat genome
Valencia-Sánchez et al. (2021) and Liu et al. (2021) provide structural and biological insights about the existence and importance of a nucleosome-like particle in a family of giant viruses.