Vannini Group
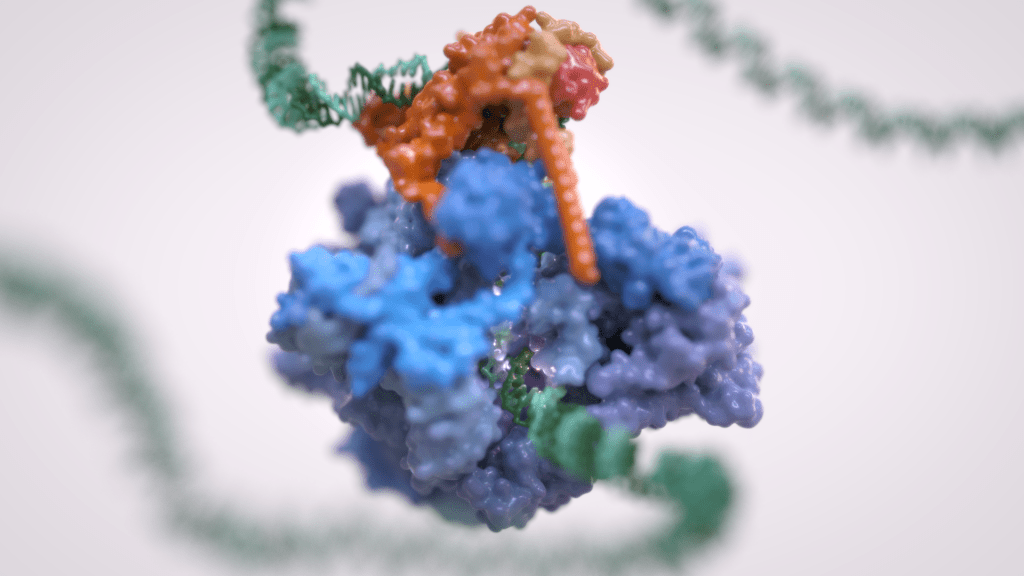
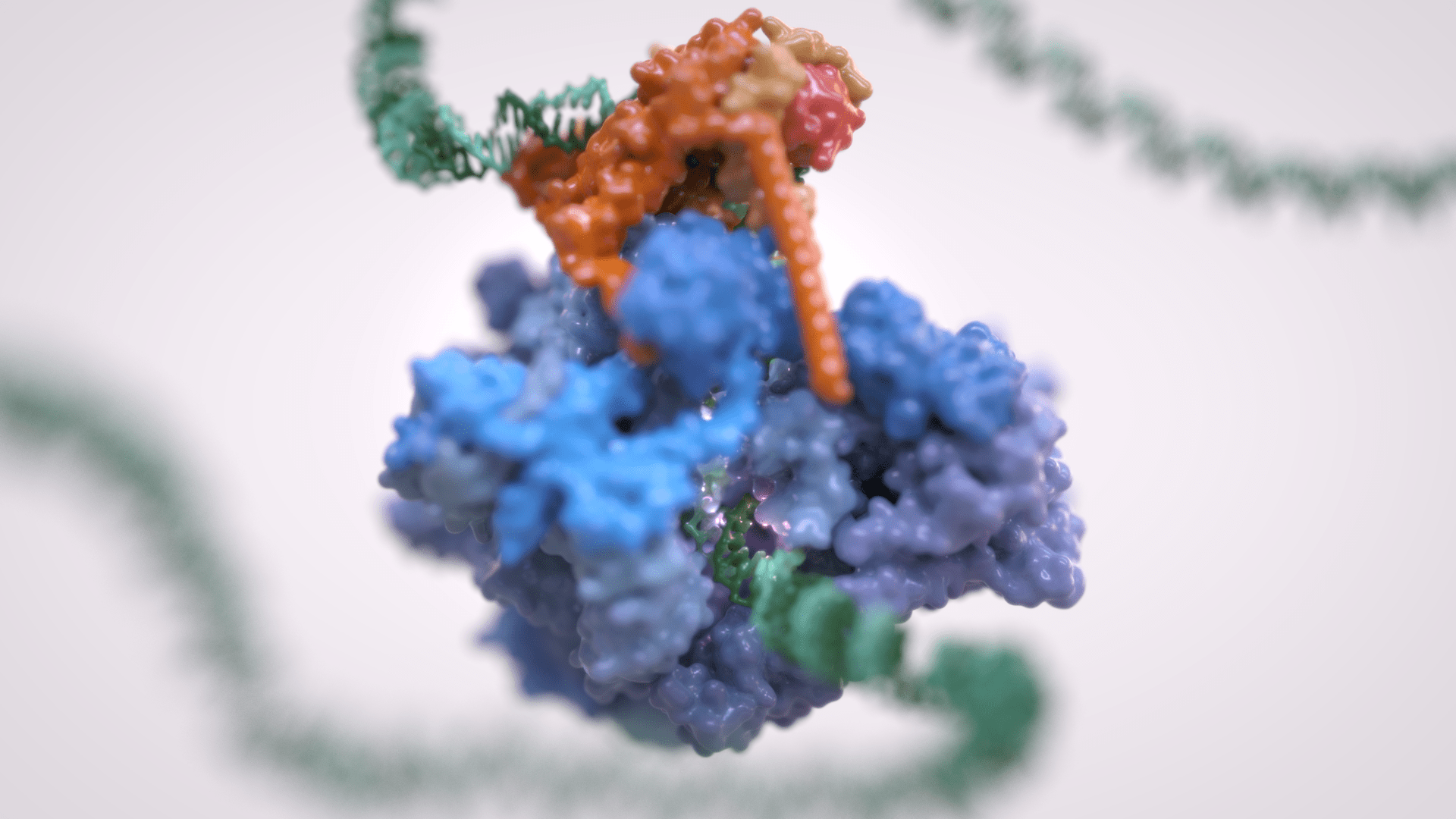
La trascrizione genica è il primo passaggio che regola l’espressione dell’informazione genetica codificata in un genoma, ed è alla base della differenziazione cellulare e dello sviluppo dell’organismo. La trascrizione genica eucariotica avviene nel contesto di genomi altamente strutturati e organizzati e coordina numerosi eventi che si verificano nel nucleo. La trascrizione eucariotica si basa su tre diverse RNA polimerasi: L’RNA polimerasi I (Pol I) trascrive l’RNA ribosomiale, l’RNA polimerasi II (Pol II) sintetizza gli RNA messaggeri e l’RNA polimerasi III (Pol III) produce RNA brevi e non tradotti, compreso l’intero pool di tRNA, che sono essenziali per la crescita cellulare.
Per molto tempo si è ritenuto che solo Pol II fosse regolata e che Pol I e Pol III non richiedessero tale controllo, essendo dedicati a geni housekeeping. Tuttavia, è ora chiaro come la trascrizione dell’RNA polimerasi III sia strettamente regolata e sia un fattore determinante per la crescita di un organismo. La deregolazione di Pol III è stata osservata in varie forme di cancro e mutazioni genetiche a carico di Pol III causano gravi malattie neurodegenerative.
Inoltre, Pol III e i suoi fattori associati svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nella struttura e nell’organizzazione del genoma. Questi “ruoli extra-trascrizionali” sono svolti attraverso interazioni con altri componenti cellulari quali i transposoni, i complessi SMC (dall’inglese Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) e i rimodellatori specifici della cromatina.
Il Vannini Group utilizza un approccio di Biologia Strutturale Integrativa, che combina analisi di crio-microscopia elettronica all’avanguardia, dati di diffrazione dei raggi X, cross-linking e spettrometria di massa nativa. Integriamo i dati strutturali con le tecniche di biologia molecolare e cellulare per ottenere una visione globale di questi processi fondamentali e di come la loro errata regolazione possa condurre a malattie oncologiche e neurodegenerative.
Membri del gruppo
-
 Alessandro Vannini
Alessandro Vannini
Head of Structural Biology Research Centre -
 Alessandro Borsellini
Alessandro Borsellini
Postdoc -
 Giacomo Ettore Casale
Giacomo Ettore Casale
Postdoc -
 Valentina Cecatiello
Valentina Cecatiello
Senior Technician -
 Sebastian Chamera
Sebastian Chamera
Postdoc -
 Fabiola Iommazzo
Fabiola Iommazzo
PhD Student -
 Thomas Noé Perry
Thomas Noé Perry
Postdoc -
 Fabio Pessina
Fabio Pessina
Senior Technician -
 Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Postdoc -
 Ewan Ramsay
Ewan Ramsay
Senior Staff Scientist -
 Ankit Roy
Ankit Roy
PhD Student -
 Syed Zawar Shah
Syed Zawar Shah
PhD Student
Pubblicazioni
-
08/2021 - Elife
Linker histone H1.8 inhibits chromatin binding of condensins and DNA topoisomerase II to tune chromosome length and individualization
DNA loop extrusion by condensins and decatenation by DNA topoisomerase II (topo II) are thought to drive mitotic chromosome compaction and individualization. Here, we reveal that the linker histone H1.8 antagonizes condensins and topo II to shape mitotic chromosome organization. In vitro chromatin reconstitution experiments demonstrate that H1.8 inhibits binding of condensins and topo II […]
-
05/2021 - Genes Dev
Mechanism of selective recruitment of RNA polymerases II and III to snRNA gene promoters
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) small nuclear RNA (snRNA) promoters and type 3 Pol III promoters have highly similar structures; both contain an interchangeable enhancer and “proximal sequence element” (PSE), which recruits the SNAP complex (SNAPc). The main distinguishing feature is the presence, in the type 3 promoters only, of a TATA box, which determines […]
-
01/2021 - Wellcome Open Res
A commercial antibody to the human condensin II subunit NCAPH2 cross-reacts with a SWI/SNF complex component
Condensin complexes compact and disentangle chromosomes in preparation for cell division. Commercially available antibodies raised against condensin subunits have been widely used to characterise their cellular interactome. Here we have assessed the specificity of a polyclonal antibody (Bethyl A302-276A) that is commonly used as a probe for NCAPH2, the kleisin subunit of condensin II, in […]
-
12/2020 - Nature Communications
Structure of human RNA polymerase III
In eukaryotes, RNA Polymerase (Pol) III is specialized for the transcription of tRNAs and other short, untranslated RNAs. Pol III is a determinant of cellular growth and lifespan across eukaryotes. Upregulation of Pol III transcription is observed in cancer and causative Pol III mutations have been described in neurodevelopmental disorders and hypersensitivity to viral infection. […]
-
10/2020 - Biochemical Society Transactions
Condensin complexes: understanding loop extrusion one conformational change at a time
Condensin and cohesin, both members of the structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC) family, contribute to the regulation and structure of chromatin. Recent work has shown both condensin and cohesin extrude DNA loops and most likely work via a conserved mechanism. This review focuses on condensin complexes, highlighting recent in vitro work characterising DNA loop formation and protein […]