Vannini Group
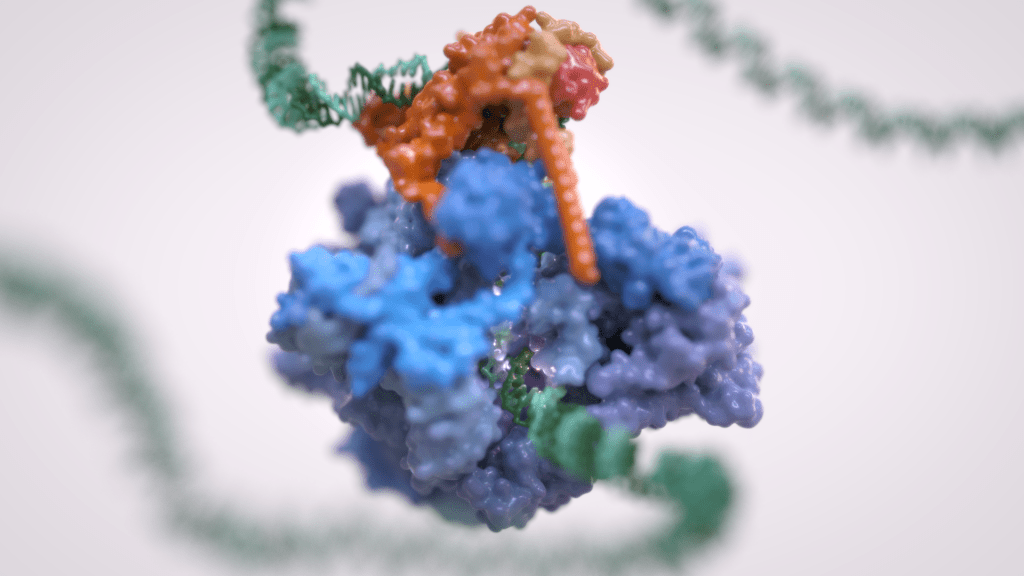
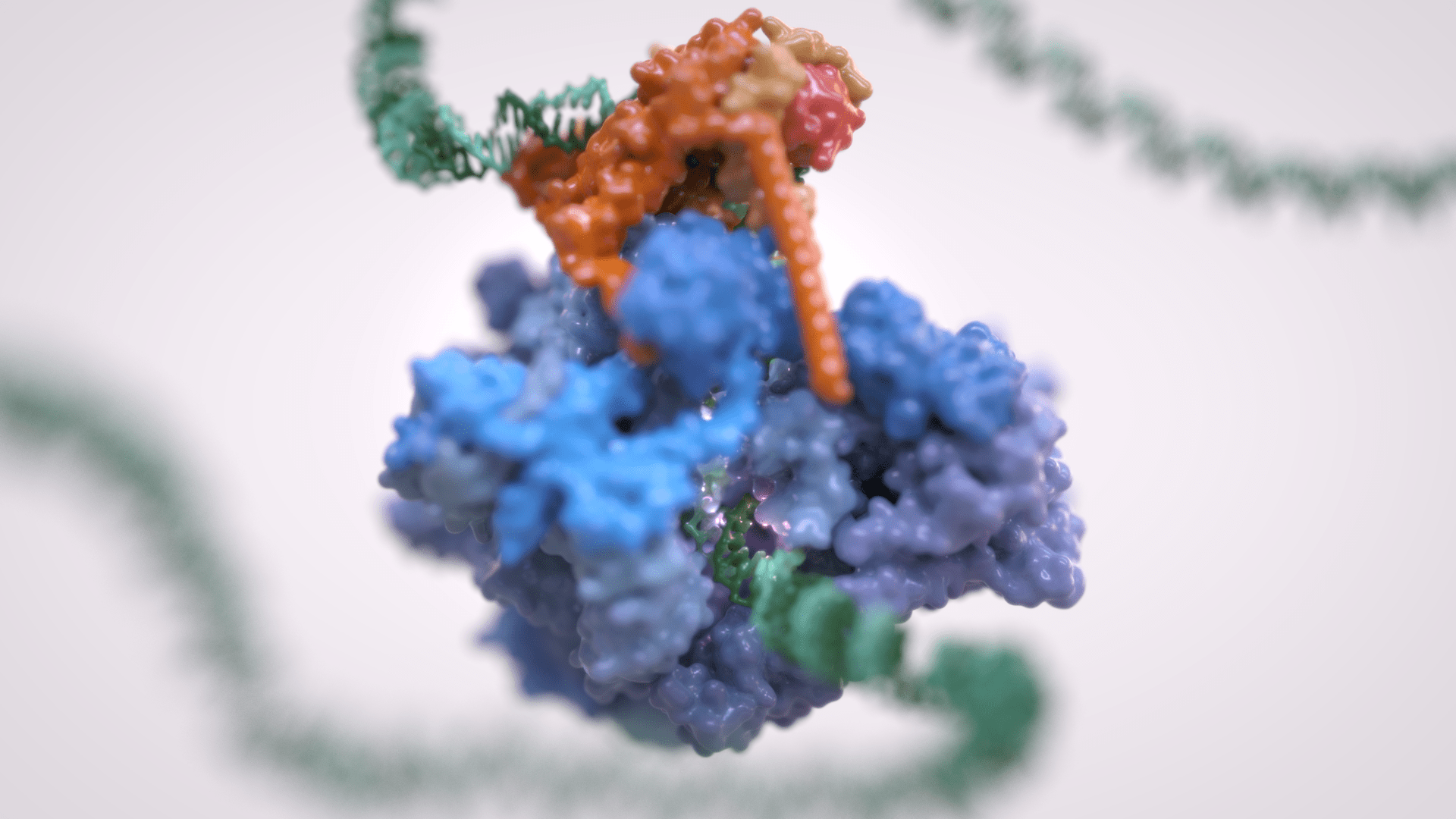
La trascrizione genica è il primo passaggio che regola l’espressione dell’informazione genetica codificata in un genoma, ed è alla base della differenziazione cellulare e dello sviluppo dell’organismo. La trascrizione genica eucariotica avviene nel contesto di genomi altamente strutturati e organizzati e coordina numerosi eventi che si verificano nel nucleo. La trascrizione eucariotica si basa su tre diverse RNA polimerasi: L’RNA polimerasi I (Pol I) trascrive l’RNA ribosomiale, l’RNA polimerasi II (Pol II) sintetizza gli RNA messaggeri e l’RNA polimerasi III (Pol III) produce RNA brevi e non tradotti, compreso l’intero pool di tRNA, che sono essenziali per la crescita cellulare.
Per molto tempo si è ritenuto che solo Pol II fosse regolata e che Pol I e Pol III non richiedessero tale controllo, essendo dedicati a geni housekeeping. Tuttavia, è ora chiaro come la trascrizione dell’RNA polimerasi III sia strettamente regolata e sia un fattore determinante per la crescita di un organismo. La deregolazione di Pol III è stata osservata in varie forme di cancro e mutazioni genetiche a carico di Pol III causano gravi malattie neurodegenerative.
Inoltre, Pol III e i suoi fattori associati svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nella struttura e nell’organizzazione del genoma. Questi “ruoli extra-trascrizionali” sono svolti attraverso interazioni con altri componenti cellulari quali i transposoni, i complessi SMC (dall’inglese Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) e i rimodellatori specifici della cromatina.
Il Vannini Group utilizza un approccio di Biologia Strutturale Integrativa, che combina analisi di crio-microscopia elettronica all’avanguardia, dati di diffrazione dei raggi X, cross-linking e spettrometria di massa nativa. Integriamo i dati strutturali con le tecniche di biologia molecolare e cellulare per ottenere una visione globale di questi processi fondamentali e di come la loro errata regolazione possa condurre a malattie oncologiche e neurodegenerative.
Membri del gruppo
-
 Alessandro Vannini
Alessandro Vannini
Head of Structural Biology Research Centre -
 Alessandro Borsellini
Alessandro Borsellini
Postdoc -
 Giacomo Ettore Casale
Giacomo Ettore Casale
Postdoc -
 Valentina Cecatiello
Valentina Cecatiello
Senior Technician -
 Sebastian Chamera
Sebastian Chamera
Postdoc -
 Fabiola Iommazzo
Fabiola Iommazzo
PhD Student -
 Thomas Noé Perry
Thomas Noé Perry
Postdoc -
 Fabio Pessina
Fabio Pessina
Senior Technician -
 Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Postdoc -
 Ewan Ramsay
Ewan Ramsay
Senior Staff Scientist -
 Ankit Roy
Ankit Roy
PhD Student -
 Syed Zawar Shah
Syed Zawar Shah
PhD Student
Pubblicazioni
-
04/2018 - Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech
Structural rearrangements of the RNA polymerase III machinery during tRNA transcription initiation
RNA polymerase III catalyses the synthesis of tRNAs in eukaryotic organisms. Through combined biochemical and structural characterisation, multiple auxiliary factors have been identified alongside RNA Polymerase III as critical in both facilitating and regulating transcription. Together, this machinery forms dynamic multi-protein complexes at tRNA genes which are required for polymerase recruitment, DNA opening and initiation […]
-
01/2018 - Nature
Structural basis of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation
RNA polymerase (Pol) III transcribes essential non-coding RNAs, including the entire pool of transfer RNAs, the 5S ribosomal RNA and the U6 spliceosomal RNA, and is often deregulated in cancer cells. The initiation of gene transcription by Pol III requires the activity of the transcription factor TFIIIB to form a transcriptionally active Pol III preinitiation […]
-
08/2017 - Transcription
New tricks for an old dog: Brf2-dependent RNA Polymerase III transcription in oxidative stress and cancer
Here, we discuss the role of Brf2, an RNA Polymerase III core transcription factor, as a master switch of the oxidative stress response. We highlight the interplay of Brf2 with the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway, as well as the role of Brf2 in cancer and other possible regulations.
-
08/2017 - EMBO J
RNA polymerase I, bending the rules?
Transcription initiation is one of the key regulatory steps in expressing the genetic information encoded in the DNA. Mechanisms of RNA Pol II transcription have been extensively studied, whereas the structural basis of RNA Pol I and III transcription is still poorly defined. Three recent studies discussed here give a first glimpse into the molecular mechanisms underlying the process of RNA Pol I transcriptional initiation and […]
-
07/2017 - Nature Communications
Molecular mechanisms of Bdp1 in TFIIIB assembly and RNA polymerase III transcription initiation
Initiation of gene transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) III requires the activity of TFIIIB, a complex formed by Brf1 (or Brf2), TBP (TATA-binding protein), and Bdp1. TFIIIB is required for recruitment of Pol III and to promote the transition from a closed to an open Pol III pre-initiation complex, a process dependent on the activity […]