Vannini Group
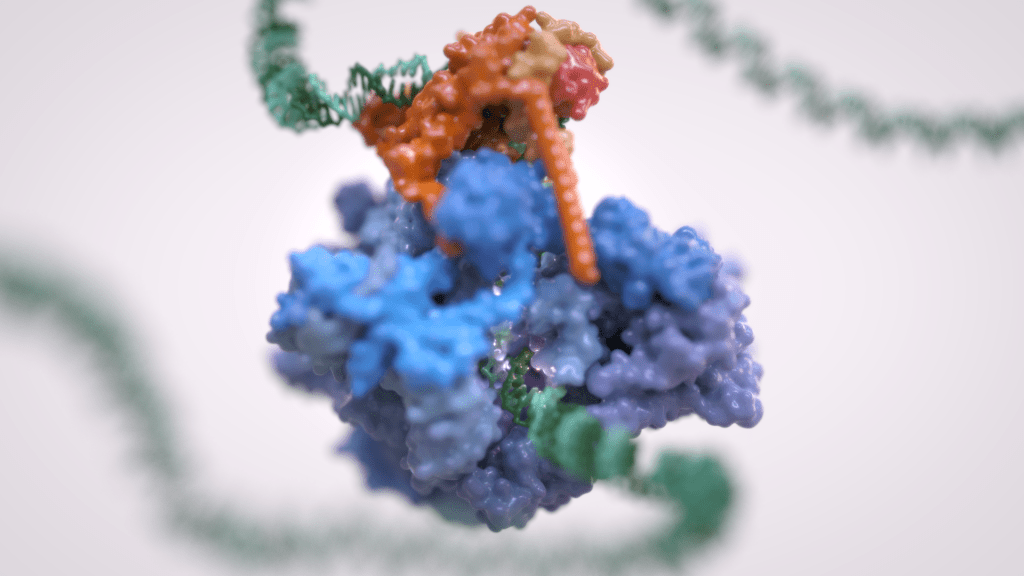
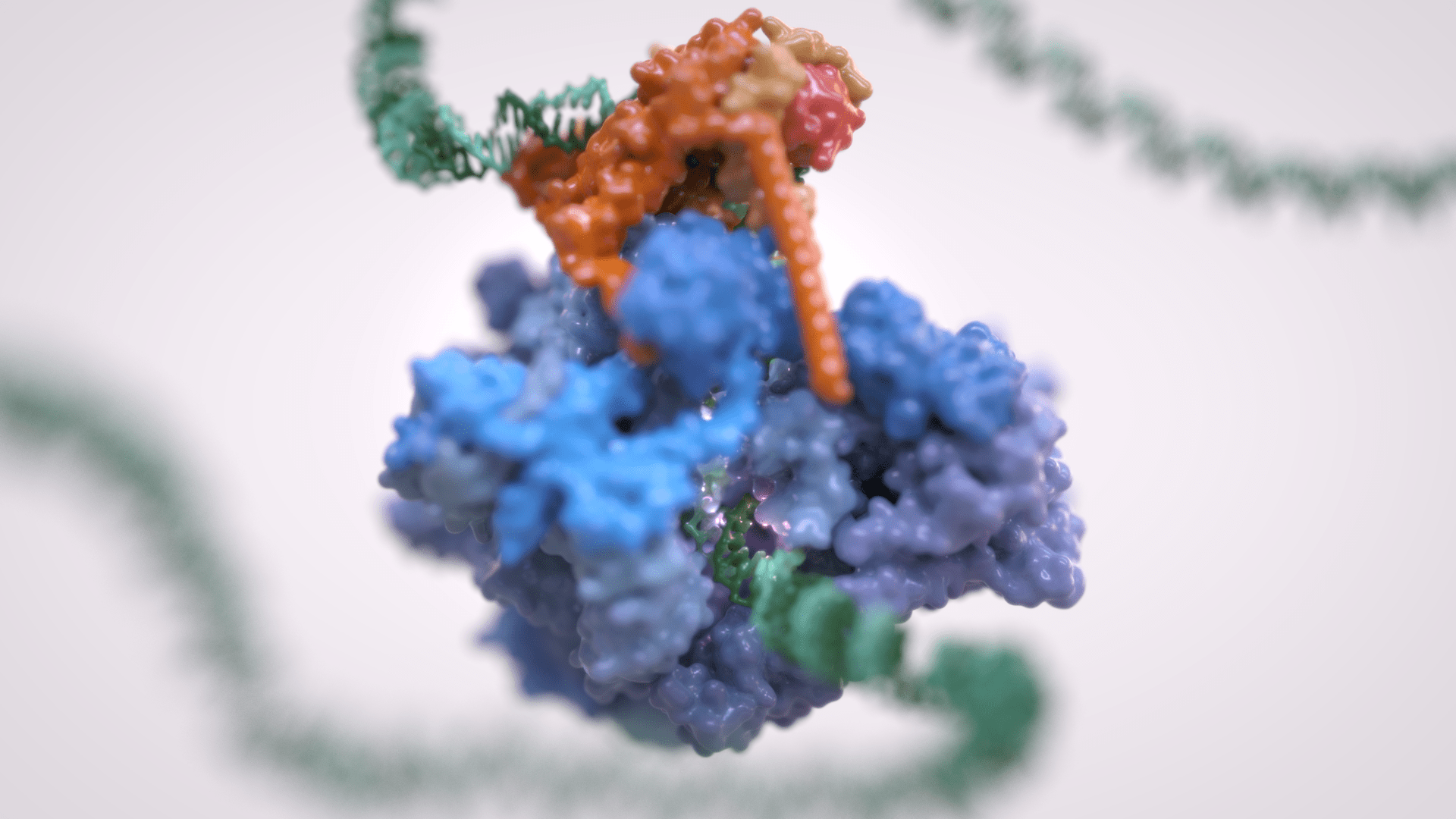
La trascrizione genica è il primo passaggio che regola l’espressione dell’informazione genetica codificata in un genoma, ed è alla base della differenziazione cellulare e dello sviluppo dell’organismo. La trascrizione genica eucariotica avviene nel contesto di genomi altamente strutturati e organizzati e coordina numerosi eventi che si verificano nel nucleo. La trascrizione eucariotica si basa su tre diverse RNA polimerasi: L’RNA polimerasi I (Pol I) trascrive l’RNA ribosomiale, l’RNA polimerasi II (Pol II) sintetizza gli RNA messaggeri e l’RNA polimerasi III (Pol III) produce RNA brevi e non tradotti, compreso l’intero pool di tRNA, che sono essenziali per la crescita cellulare.
Per molto tempo si è ritenuto che solo Pol II fosse regolata e che Pol I e Pol III non richiedessero tale controllo, essendo dedicati a geni housekeeping. Tuttavia, è ora chiaro come la trascrizione dell’RNA polimerasi III sia strettamente regolata e sia un fattore determinante per la crescita di un organismo. La deregolazione di Pol III è stata osservata in varie forme di cancro e mutazioni genetiche a carico di Pol III causano gravi malattie neurodegenerative.
Inoltre, Pol III e i suoi fattori associati svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nella struttura e nell’organizzazione del genoma. Questi “ruoli extra-trascrizionali” sono svolti attraverso interazioni con altri componenti cellulari quali i transposoni, i complessi SMC (dall’inglese Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) e i rimodellatori specifici della cromatina.
Il Vannini Group utilizza un approccio di Biologia Strutturale Integrativa, che combina analisi di crio-microscopia elettronica all’avanguardia, dati di diffrazione dei raggi X, cross-linking e spettrometria di massa nativa. Integriamo i dati strutturali con le tecniche di biologia molecolare e cellulare per ottenere una visione globale di questi processi fondamentali e di come la loro errata regolazione possa condurre a malattie oncologiche e neurodegenerative.
Membri del gruppo
-
 Alessandro Vannini
Alessandro Vannini
Head of Structural Biology Research Centre -
 Alessandro Borsellini
Alessandro Borsellini
Postdoc -
 Giacomo Ettore Casale
Giacomo Ettore Casale
Postdoc -
 Valentina Cecatiello
Valentina Cecatiello
Senior Technician -
 Sebastian Chamera
Sebastian Chamera
Postdoc -
 Fabiola Iommazzo
Fabiola Iommazzo
PhD Student -
 Thomas Noé Perry
Thomas Noé Perry
Postdoc -
 Fabio Pessina
Fabio Pessina
Senior Technician -
 Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Mariavittoria Pizzinga
Postdoc -
 Ewan Ramsay
Ewan Ramsay
Senior Staff Scientist -
 Ankit Roy
Ankit Roy
PhD Student -
 Syed Zawar Shah
Syed Zawar Shah
PhD Student
Pubblicazioni
-
06/2004 - J Biol Chem
Crystal structure of the quorum-sensing protein TraM and its interaction with the transcriptional regulator TraR
Transfer of the tumor-inducing plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens is controlled by a quorum-sensing system whose main components are the transcriptional regulator TraR and its autoinducer. This system allows bacteria to synchronize infection of the host plant when a “quorum” of cells has been reached. TraM is an A. tumefaciens protein involved in the regulation of […]
-
02/2004 - Biochemistry
Mechanism of activation of human heparanase investigated by protein engineering
The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of activation of human heparanase, a key player in heparan sulfate degradation, thought to be involved in normal and pathologic cell migration processes. Active heparanase arises as a product of a series of proteolytic processing events. Upon removal of the signal peptide, the resulting, poorly […]
-
01/2004 - Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the quorum-sensing regulator TraM from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
TraM is a 11.4 kDa protein involved in the control of the conjugal transfer of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmids by quorum-sensing. TraM was overexpressed and purified from Escherichia coli. This protein binds to the transcriptional regulator TraR, abolishing its function. Size-exclusion chromatography and dynamic light scattering show that the recombinant protein has an apparent molecular […]
-
10/2002 - Analytical Chemistry
Determination of the stoichiometry of noncovalent complexes using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry
An electrospray mass spectrometry-based methodology has been developed to have a fast and sensitive method for protein-cofactor stoichiometry determination. As model systems, we used two proteins which require the presence of cofactors for activity: TraR, a member of the LuxR family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators, which requires an acyl-homoserine lactone molecule called Agrobacterium autoinducer (AAI) […]
-
09/2002 - EMBO J
The crystal structure of the quorum sensing protein TraR bound to its autoinducer and target DNA
The quorum sensing system allows bacteria to sense their cell density and initiate an altered pattern of gene expression after a sufficient quorum of cells has accumulated. In Agrobacterium tumefaciens, quorum sensing controls conjugal transfer of the tumour- inducing plasmid, responsible for plant crown gall disease. The core components of this system are the transcriptional […]